Photovoltaic cells are used to convert photons streaming from the Sun into photovoltaic (PV) energy or “Solar Electricity”.
“I’d put my money on the sun and solar energy. What a source of power! I hope we don’t have to wait until oil and coal run out before we tackle that.” Thomas Edison, 1931
Well, 80 years later, Solar photovoltaic (PV) energy became widely recognized as a crucial component in addressing our worldwide need for secure, affordable and renewable energy, hence quickly becoming the energy option of choice worldwide. The advantages of using solar power for us, our businesses and the environment are compelling and easy to understand.
With the enormous benefits of using the Solar Power, it was just logical for President Obama to introduce many programs to encourage Americans to utilize the Solar Energy in their homes and businesses.
California has also been on the forefront of promoting the use of the Solar Power by its famous “Million Solar Roofs Program.” In this program, California has set a goal to create 3,000 megawatts of new, solar-produced electricity by 2017. The idea is to move the state toward a cleaner energy future and to help lower the cost of solar systems for consumers. In 2018, Governor Brown of California signed a memorandum to make California a 100% Green Energy State by 2040.
The rapidly increasing cost-competitiveness of solar energy is creating attractive opportunities for capital providers interested in infrastructure investment.
With many countries reliant on costly energy imports and unsustainable fossil fuels, investment in renewables is now double that of coal and gas combined. Solar PV global capacity continues to rise exponentially and has made staggering progress in the last two decades. In recent years, investment in renewables has often outperformed traditional energy stocks, and this is set to continue as PV, alongside onshore wind, are “winning the cost race” and becoming our cheapest energy option by 2020 (Bloomberg New Energy Finance, Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment. 2016).
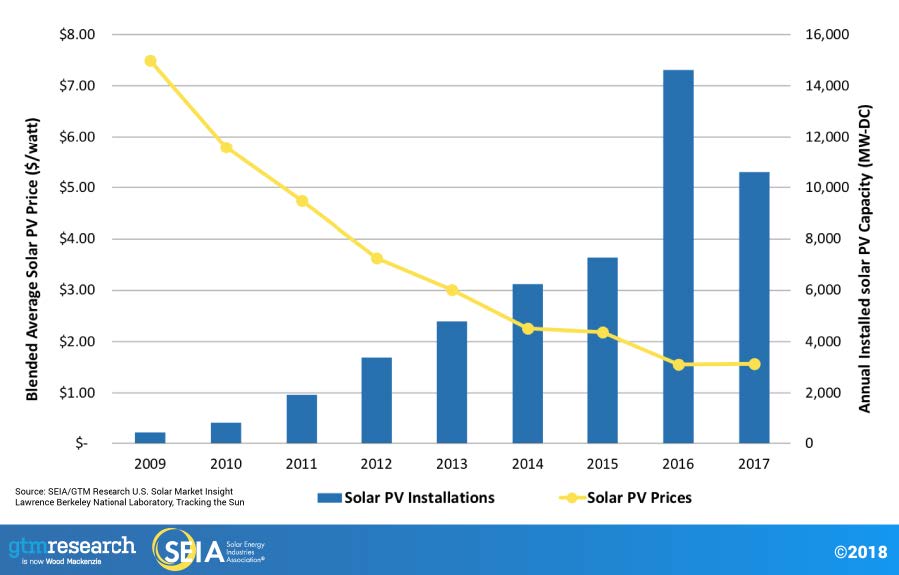
THE RATE IN WHICH THE COST OF SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAICS FALLING DOWN HAVE MADE SOLAR MORE AFFORDABLE THAN EVER. THE AVERAGE PRICE OF A COMPLETED PV SYSTEM HAS DROPPED BY 59 PERCENT OVER THE LAST DECADE.


Through 2018, there are more than 64 GW of Solar installed in the U.S., enough to power more than 12.3 million homes. Over the last decade, the solar market in the United States has grown at an average rate of 50% each year. There are nearly 2 million individual solar installations in the U.S., ranging from small home rooftop systems to large utility-scale systems that add hundreds of megawatts of clean electricity to the power grid.
There is no doubt that Solar Technology represents the future of universal power. First Energy Systems took the challenge of making the Solar Systems both affordable and accessible by introducing innovative solar products to cover all aspects of life, from personal products to complete turn key projects.
OUR OFFERINGS IN THE USA INCLUDE:
-
Commercial / Industrial Solar Power Systems
-
Solar Farms
-
Solar Assembly Lines
-
Solar Consumer Products
-
Home Solar Power Systems
-
Solar Home Products
OUR OFFERINGS OVERSEAS INCLUDE:
-
Solar Relief Products
-
Consulting and Turn Key Projects
-
Solar Farms (Build & Operate)
-
Solar Assembly Lines
What is a Solar Power System?
SOLAR SYSTEMS ARE MADE OF:
-
Solar-powered photovoltaic (PV) panels,
-
Charge Controller,
-
Inverters, and,
-
Battery Backup units (optional)
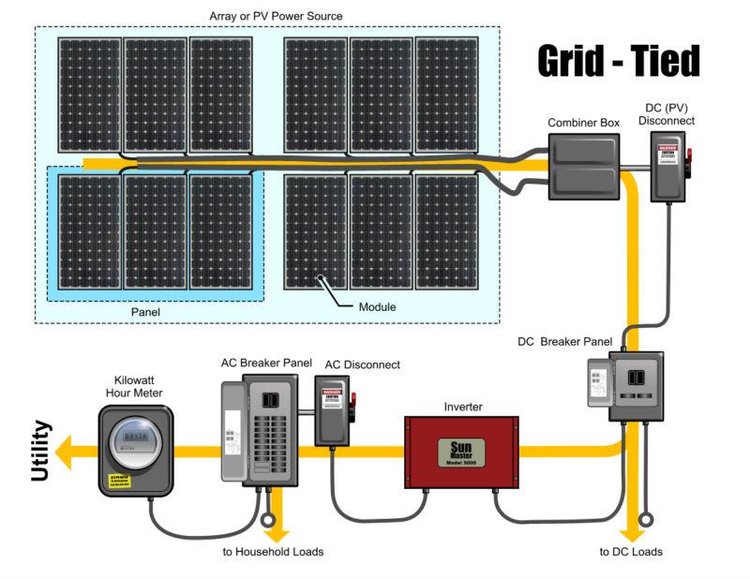
Solar-Powered Photovoltaic (PV) panels convert the sun rays into Direct Current (DC) power. A charge controller prevents the batteries from being overcharged. Inverters convert DC power into Alternate Current (AC) power which is then can be used to supply renewable energy to homes and businesses.
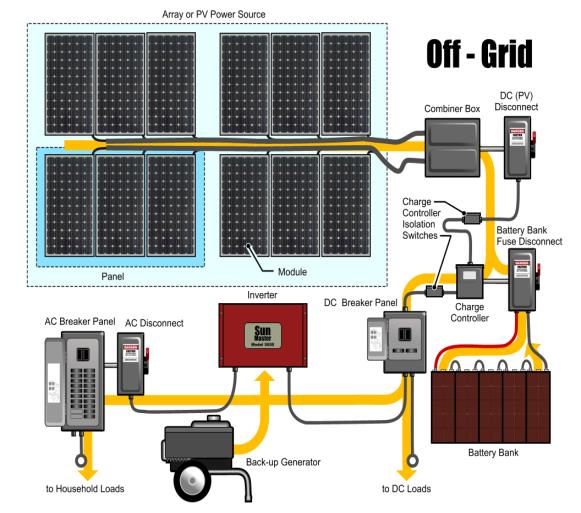
Battery Backup units are optional addition and normally needed for Off-Grid systems to supply power during the period where sunlight is not available and also can be used with On-Grid systems during emergencies. Battery Backup units are also increasingly used with commercial systems to reduce highly priced demand charges.
Solar Power Systems can be categorized in different methods:
-
by how the electricity is distributed,
-
by the way they are installed
-
By their mobility,
-
by the size of the system and,
-
by the technology used.
SOLAR POWER SYSTEMS IN TERMS OF
In terms of way of distributing the generated solar electricity, solar power systems can be divided into two categories:
-
On-Grid Power Systems (often called Grid-Tied) are those systems (Solar, Wind or, Hybrid) that are connected to the main power grid (network) in town to supply the needed energy when the said systems are not functional.
-
Off-Grid Power Systems are those systems that are not connected to the main power grid (network) in town, and therefore most of the time they include an additional Battery Backup System to supply the needed energy when the said systems are not functional.
These batteries are normally charged from the systems themselves or thru other means like gasoline generators if needed.
Based on the way they are installed; Solar Farms can be: Ground Installed, Roof Installed or, Water Installed (Floating)

On-Roof Solar Farm Installation

On-Ground Solar Farm Installation

Solar Floating Farm, within Water Treatment Plant

On-Roof Home Solar System Installation

On-Ground Home Solar System Installation

Solar Floating Farm, where land availability is low
Based on mobility, Solar Farms can be as Fixed-Angel Installs or Changing-Angel installs (Tracking the sun movements). In general, Solar Farms with Tracking Systems would cost 20% – 30% more than Stationary Farms, but they generate around 30% more power and use 20% – 40% less land to accommodate.
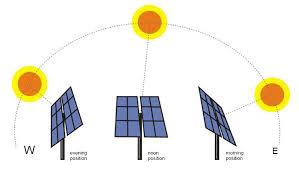
Solar – Tracking System Principle

Intelligent Solar-Tracking Farm
Also, for all practical reasons, we can divide the Solar Power Systems into FIVE categories, based on their usage as follows:
-
Up to 1,000 W (Micro Systems) are good for Emergency usage.
-
Up to 5 KW (Mini Systems) those fit the need of Small Homes / Businesses.
-
Up to 10 KW (Small Systems) suitable for medium Homes / Businesses and small commercials.
-
Up to 100 KW (Medium Systems) suitable for medium Businesses and small Industrial facilities.
-
Up to 1,000 KW (Large Systems) are good for medium Commercial use (including Schools, Hospitals)
-
Up to 25 MW (Commercial Systems) are used for larger establishments (Malls, Factories even small Towns) supply whole towns).
-
25 MW + (Utility Systems or Solar Farms) are used to power up Towns and Cities and to make up a Country Power Grid System.
In terms of Technology used, Solar Power Systems can be harnessed by three different technologies:
-
Photovoltaics (PV), which directly convert light to electricity;
-
Concentrating solar power (CSP), which uses heat from the sun (thermal energy) to drive utility-scale, electric turbines; and
-
Solar heating and cooling (SHC) systems, which collect thermal energy to provide hot water and air heating or conditioning.
Research labs in many countries are working day and night to develop more sophisticated, more advanced and, cheaper technologies to generate solar power. The future is very promising for this exciting technology.

Solar Thermal Panels For Heating & Cooling